Describe The Anatomy Of Eyeball
The white visible portion of the eyeball. Ciliary Body Structure containing muscle and is located behind the iris which focuses the lens.
 Anatomy And Movement Of The Eye Doctor Stock In 2020 Eye Anatomy Eyeball Anatomy Skull Anatomy
Anatomy And Movement Of The Eye Doctor Stock In 2020 Eye Anatomy Eyeball Anatomy Skull Anatomy
The eye is shaped like a round ball with a slight bulge at the front.

Describe the anatomy of eyeball. The orbit is formed by the cheekbone the forehead the temple and the side of the nose. The posterior pole of the eyeball is connected with the optic nerve CN II which conveys the information from the retina to the brain. The eye has three main layers.
Anatomy of the Eye. The eye is cushioned within the orbit by pads of fat. The eyeball is a bilateral and spherical organ which houses the structures responsible for vision.
Ophthalmic artery à retinal artery. Conjunctiva - The conjunctiva is a mucus membrane that covers the surface of the eye and the inner part of the eyelids. The eye is part of the sensory nervous system.
The sclera is outermost layer of the eyeball. Eyeball spheroidal structure containing sense receptors for vision found in all vertebrates and constructed much like a simple camera. The human eyeball is nearly a spherical structure.
It lies in a bony cavity within the facial skeleton - known as the bony orbit. The muscles that move the eyeball are attached to the sclera. It describes in depth the different parts of the eye that are involved in the ocular manifestations seen in the mucopolysaccharidoses MPS.
The wall of the eyeball is three-layered. A series of fibers that connects the ciliary body of the eye with the lens holding it in place. Fibrous vascular pigmented and nervous retina.
With the sclera as the outer layer continuous with the cornea choroid as the middle vascular layer continuous with the ciliary body and iris and the retina as the innermost layer. From their origin the oblique muscles take an angular approach to the eyeball in contrast to the straight approach of the recti muscles. Layer containing blood vessels that lines the back of the eye and is located between the retina the inner light-sensitive layer and the sclera the outer white eye wall.
The eyeball houses the retina an extremely metabolically active layer of nerve tissue made up of millions of light receptors photoreceptorsand all of the structures needed to focus light onto it. The eyeball is set in a protective cone-shaped cavity in the skull called the orbit or socket This bony orbit also enlarges as the eye grows. Functionally the most important layer is the retina which receives the external visual stimuli.
A ping-pong ball is about 1½ inch in diameter which makes the average adult eyeball about 23 the size of a ping-pong ball. In addition to the eyeball itself the orbit contains the muscles that move the eye blood vessels and nerves. You can study the anatomy of the eyeball in detail through these study units.
Anatomy of the Eye. The eyeball consists of three layers. The human eye is a paired sense organ that reacts to light and allows vision.
A pair of eyes is located in sockets of the skull known as orbits. The wall is formed by three layers. These layers lie flat against each other and form the eyeball.
The outer layer of dense connective tissue forms sclera. They attach to the posterior surface of the sclera. The sclera is the part of the eye commonly known as the white It forms the supporting wall of the eyeball and is continuous with the clear cornea.
The inner layer of the eyeball and contains the optic portion and non-visual retinaThe optic portion is further divided into two layers known as the neural layer and pigment cell layer. The eyeball and its functional muscles are surrounded by a layer of orbital fat that acts much like a cushion permitting a smooth rotation of the eyeball about a virtually fixed point the centre of rotation. The outer layer of the eyeball is a tough white opaque membrane called the sclera the white of the eye.
The transparent anterior portion of this layer is termed as the cornea. The protrusion of the eyeballsproptosisin exophthalmic goitre is caused by the collection of fluid in the orbital fatty tissue. At the front of the eyeball the sclera becomes the cornea.
Suspensory ligament of lens. Muscles responsible for moving the eyeball are attached to the eyeball at the sclera. Cornea - The cornea is the clear dome-like structure on the front part of the eyeThe cornea delivers 23 of the refracting power to the eye.
Anatomically the eyeball can be divided into three parts - the fibrous vascular and inner layers. It is the white and opaque part of the eyeball. The cornea is the transparent dome-shaped part of the eyeball.
Rod and cone cells in the retina are photoreceptive cells which are able to detect visible light and convey this information to the brainEyes signal information which is used by the brain to elicit the perception of color shape depth movement and other features. The neural layer of the optic portion of the retina is light receptive and the pigment cell layer helps to reduce the scattering of light. The sclera is covered by the conjunctiva a.
The orbit is the bony eye socket of the skull.
 Eyeball Anatomy Eyeball Anatomy Anatomy Eye Anatomy
Eyeball Anatomy Eyeball Anatomy Anatomy Eye Anatomy
 Human Eye Ball Anatomy Physiology Diagram
Human Eye Ball Anatomy Physiology Diagram
 The Eye Diagram And Functions Functions Of The Human Eye Anatomy Body System Human Eye Diagram Eye Anatomy Diagram Of The Eye
The Eye Diagram And Functions Functions Of The Human Eye Anatomy Body System Human Eye Diagram Eye Anatomy Diagram Of The Eye
 Cranial Nerves Optic Nerve Cn 2 Sensory Only Receptors In The Retina Rods Cones Synapse With Bipolar Cranial Nerves Nerve Anatomy Brain Anatomy
Cranial Nerves Optic Nerve Cn 2 Sensory Only Receptors In The Retina Rods Cones Synapse With Bipolar Cranial Nerves Nerve Anatomy Brain Anatomy
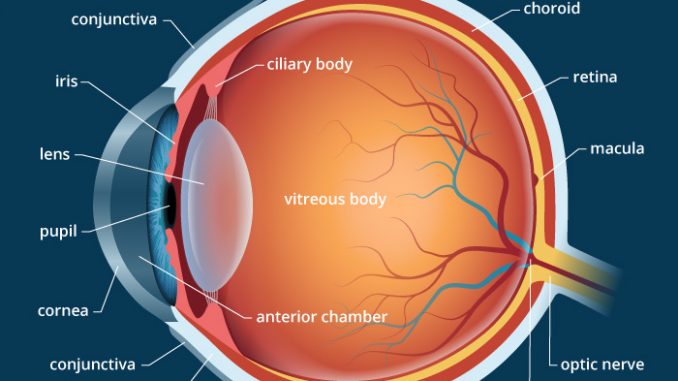 Human Eye Anatomy Parts And Structure Online Biology Notes
Human Eye Anatomy Parts And Structure Online Biology Notes
 Anatomy And Physiology Of The Eye Functions Of The Parts Of The Eye Anatomy And Physiology Physiology Parts Of The Eye
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Eye Functions Of The Parts Of The Eye Anatomy And Physiology Physiology Parts Of The Eye
 Eye Anatomy Animated Sponsored Aff Anatomy Eye Characters Animated Eye Anatomy Anatomy Face Muscles Anatomy
Eye Anatomy Animated Sponsored Aff Anatomy Eye Characters Animated Eye Anatomy Anatomy Face Muscles Anatomy
 Ora Serrata Google Search Vitreous Humour Things Under A Microscope Arteries
Ora Serrata Google Search Vitreous Humour Things Under A Microscope Arteries
 Instant Anatomy Head And Neck Areas Organs Eye Orbit Ciliary Body Anterior Eyeball Medicine Notes Medical App Optometry Education
Instant Anatomy Head And Neck Areas Organs Eye Orbit Ciliary Body Anterior Eyeball Medicine Notes Medical App Optometry Education
 Jesu Li Slozeni Organi Poput Nasih Ociju Nastajali Postupno Evolucijski I Jesu Li Nase Oci Lose Dizajnirane Kako Nas Pokusavaju Eye Anatomy Eye Health Eye Care
Jesu Li Slozeni Organi Poput Nasih Ociju Nastajali Postupno Evolucijski I Jesu Li Nase Oci Lose Dizajnirane Kako Nas Pokusavaju Eye Anatomy Eye Health Eye Care
 Module 1 Labeled Diagram Of The Eye Diagram Of The Eye Dot Worksheets Eye Anatomy
Module 1 Labeled Diagram Of The Eye Diagram Of The Eye Dot Worksheets Eye Anatomy
 2010 In Review Eye Anatomy Anatomy Human Eye
2010 In Review Eye Anatomy Anatomy Human Eye
 Awesome Anatomy Eye See Worksheet Education Com Science Worksheets Life Science Human Anatomy And Physiology
Awesome Anatomy Eye See Worksheet Education Com Science Worksheets Life Science Human Anatomy And Physiology
 00399 Jpg 1135 1041 Eye Anatomy Optometry Eye Health
00399 Jpg 1135 1041 Eye Anatomy Optometry Eye Health
 Use Crayola Crayons Colored Pencils Or Markers To Color The Parts Of The Human Eye Use The Word Bank Below To Identify P Biyoloji Ortaokul Boyama Sayfalari
Use Crayola Crayons Colored Pencils Or Markers To Color The Parts Of The Human Eye Use The Word Bank Below To Identify P Biyoloji Ortaokul Boyama Sayfalari
 Well Eye Anatomy Inner Ear Disorders Sensory System
Well Eye Anatomy Inner Ear Disorders Sensory System
Eye In Cross Section Anatomy The Eyes Have It
 The Eye And Vision Rectus Muscle Anatomy And Physiology Autonomic Nervous System
The Eye And Vision Rectus Muscle Anatomy And Physiology Autonomic Nervous System

Post a Comment for "Describe The Anatomy Of Eyeball"